Both of these treatments are meant for shallow exfoliation of the very superficial layers of skin, in order to improve skin texture, clear pores, reduce oiliness, help with sun damage (benign photo pigmentation and *melasma), by increasing the skins cellular turnover and stimulating the production of collagen, reducing very fine lines and wrinkles. Deep wrinkles or extensive sun damage are better addressed with the use of lasers (see IPL, Affirm Multiplex, and Smartxide DOT fractional CO2 resurfacing in the Lasers and Light Therapy section)
* see also separate section on Melasma (Brown Spots)
Microdermabrasion
There are 2 types of microdermabrasion machines in common usage; 1 type which blasts the surface of the skin with aluminium oxide crystals, and the other which uses a wand tipped with very fine diamond crystals to gently exfoliate the superficial dead cells.
At The Lazer Room, we use the diamond wand, due to concerns of potential embedding of crystals in the skin and possible linkage of aluminium toxicity with Alzheimer’s disease.
Treatment with the DiamondTome is a very gentle process. The wand is lightly rubbed over the surface of the skin, sloughing away dead cells, while suctioning the contents of blocked pores, leaving a smooth, fresh, ultra clean feeling. Besides the face, neck, and decolletage, other areas where there is a build-up of dead skin cells may also be treated such as Keratosis pilaris found on the backs of the arms and legs.
Keratosis Pilaris
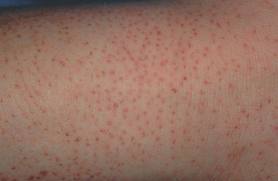 A benign condition that may run in families, more commonly found in people with dry skin or eczema.
A benign condition that may run in families, more commonly found in people with dry skin or eczema.
Keratosis Pilaris appears as rough pink sandpapery goose bumps on the back of the upper arms and thighs, it is also occasionally seen on the face.
Treatment: Moisturisers containing urea. May also respond to creams containing glycolic, lactic or salicylic acids ; topical tretinoin (vitamin A derivative) or vitamin D creams.
Microdermabrasion will smooth the roughness, and allow better penetration of above creams.
Rationale for Microdermabrasion
Aside from removing dead skin cells and of vacuuming out blocked pores:
- Studies show thickening of the epidermis and an increase in collagen formation in the dermis following a series of microdermabrasion treatments. These histological changes will be reflected in clearer, less delicate skin, with a reduction in very fine lines and wrinkles.(note: Microdermabrasion is not helpful for deeper or dynamic wrinkles)
- The top layer of the skin forms a protective barrier, prohibiting many active ingredients found in cosmecuticals from penetrating to the deeper layers of the skin. Removal of the top dead layer of skin cells allows for better penetration of nourishing creams, containing vitamins and antioxidants.
Microdermabrasion can also be used as:
- A precursor to light chemical peels (e.g. AFA Clay peel), allowing deeper penetration of cosmeceuticals to pigmented layers of skin.
- A preparation for mesoglow facials, where micropenetration of the dermis by dermal rollers allows mesotherapy cocktails of Hylaronic Acid, Essential Vitamins, Minerals and Antioxidants to further enhance the rejuvenation process. (See Injectables; Mesotherapy: Mesoglow facials)
Who Is Not A Candidate For Microdermabrasion?
- Anyone with inflamed pustules, cold sores, eczema or psoriasis plaques in the area to be treated.
- Persons with active/uncontrolled rosacea, or severe telangiectasia (facial capilliaries).
- Pregnant or lactating women, the hormonal status may predispose these persons to hyperpigmentation.
- Persons with a tendency to hypertrophic (keloid) scarring.
- Persons who have been treated with Accutane or other oral retinoids in the preceding 6-12 months.
- Caution is advised with recent treatment with acid peeling agents (e.g. glycolic, retinoic, alpha-hydroxyl -acids); although in certain cases, (see above) microdermabrasion can be used as a preparation for light chemical peels.
Chemical Peels
The main purpose of chemical peels is to accelerate the exfoliation of superficial skin cells, thereby improving the texture of the skin. Some studies have indicated that deeper chemical peels can increase collagen formation and the deposition of glycosaminoglycans in the dermis, thereby positively increasing the thickness of the skin, improving fine lines and wrinkles and improving some types of superficial scarring. Some peels are specifically used for their effects on pigmented skin (e.g. in the treatment of melasma, see glycolic , light TCA or AFA peels).
Agents Used In Chemical Peels:
- Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs-eg glycolic, lactic acids)
- Amino Acid Fillagrin Antioxidants (AFAs)
- Salicylic Acid
- Trichloracetic Acid (TCA)
- Jessner’s Solution
- Resorcinol, Pyruvic Acid, Phenol (not often used for the risks of toxicity and permanent hypopigmentation)
Levels Of Peels:
- Very Superficial Exfoliation: Affects only the most superficial part of the epidermis (stratum corneum)
- Superficial: Part or all of the epidermis.
- Medium: The epidermis and part of the uppermost layer of the dermis (papillary)
- Deep: The deep (reticular) dermis
Who Is Best Suited To Peels?
Deeper peels are needed to treat more severe degrees of damage. Sun damage can be confined to the top layer of the skin (e.g. freckles, sun spots and dull rough skin texture): or may be more extensive including seborrheic keratoses, actinic keratoses, increased wrinkling, dry, thin skin. At its most severe, photodamage will manifest as pebbly, leathery skin, with deep wrinkles, and textured brown spots.
Fitzpatrick Skin Typing
A method used to assess the risk of dyschromia (colour change) following peels. Skin types 1- 3 (pale skin types) are good candidates for chemical peels and almost never develop post -inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Whereas type 4 -6 (tanned and dark-skinned persons) are at risk.
Superficial and medium depth peels rarely cause permanent hypopigmentation (i.e. permanent lightening of the skin); whereas phenol-containing peels increase this risk dramatically.
Factors Influencing The Depth Of The Peel:
- The agents or agents used.
- The concentration/percentage of the agent(s).
- The pH (potential of hydrogen) of the peeling agent,
- The duration of contact of the chemical with the skin.
- How many layers of the agent are applied.
- How the skin was cleansed to remove the superficial oils before applying the peel.
- If the skin was pretreated in the weeks before the peel (eg. with Retin A)
- The type of skin the patient has (eg. thin/thick)
- The anatomic location of the peel (e.g. face, back, decolletage)
Examples Of Superficial And Medium Depth Peels
Superficial Peels:
AFAs: Glycolic/Lactic Acid 10-50% applied briefly; 10%-30%TCA
Medium Depth Peels:
Glycolic Acid 70% applied for longer periods of time; TCA 35-50%; Jessner’s Solution
Deep Peels:
Phenol
Specific Peels
AFAs are derived from naturally occurring amino acids in the stratum corneum (superficial layer of the epidermis), which are the main factor responsible for moisture retention. They are also potent antioxidants and natural UV filters. They are non- irritating and are particularly safe for use in persons with darker skin as there has been no recorded case of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation associated with their use.
They are particularly useful for dealing with photopigmentation (benign brown spots caused by sun damage), and may also diminish the appearance of fine facial capillaries. We have also seen a significant reduction in melasma following a 12 week course of treatment.
AFA Clay peels are categorized as superficial/light peels, with no irritation and no downtime.
They are usually administered as a series of 6 in-office peels, at 2 week intervals. The skin is prepared by a light microdermabrasion, followed by the application of a clay mask containing Dead Sea Minerals, followed by the application of the AFA acid gel and finished with a rich oil-free AFA-containing moisturiser, which hydrates the freshly treated skin.
There is an immediately noticeable improvement in skin texture and luminosity – so much so that I have taken to referring to it as my “Baby Soft Skin peel “
The in-office treatment is complemented by a simple home skin care regimen; consisting of an AFA cleanser, oil-free moisturiser and acid gel used nightly.
Pre And Post-Treatment Considerations:
Do not have this procedure done if you are having AHA (glycolic or lactic acid) peels, or have been using Retin A, Vitamin A Acid Gel, Adapalene orTazorac up to a week prior. This procedure is not suited to anyone having ablative laser treatments (e.g. CO2 or Erbium laser) but can be used in conjunction with IPL.
Sunscreen 45-60 SPF should be used throughout the duration of the treatments.
Glycolic Peels
Suitable for oily skin, *acne, and acne -prone skin, including active acne, large pores, comedones (black or whiteheads) and mild inflammatory hyperpigmented acne scars. these are usually done in a series of 6-10 treatments at increasing strength (ie 10-70% glycolic acid). Can also be useful in higher strengths for very fine lines and wrinkles or rough texture. Persons with rosacea may find higher strength glycolic acid peels irritating.
* see cautions below re Accutane, Vitamin A/Differin Gels
TCA Peels
Traditionally done for pigmentation problems, photo pigmentation and melasma. These can be superficial (10-30%), or medium depth (35-50%). Persons undergoing the higher strength TCA peels may experience flushing of the skin and a slight increase in heart rate. They will also have significant downtime related to redness and peeling of skin post procedure.
Higher strength TCA peels are not recommended for persons with dark skin, due to the risk of post inflammatory hyperpigmentation. To reduce this risk, olive or tanned skin tones should be pre-treated with skin lightening creams for a month prior.
Cautions
When should Chemical peels be avoided
- In pregnant or lactating women.
- If you have sunburned skin.
- In the presence of psoriasis, dermatitis or open sores in the treatment area.
- If you have been treated with Accutane within the preceding 6 -12 months.
- If you have had a cold sore within the preceding 10 days a prophylactic medication may be prescribed).
Medium Depth chemical peels such as Salicylic Acid/ Jessner’s /TCA may not be advised for persons:
- Using Retin A/Vitamin A Acid Gels within the past 3 months.
- Who have had a cold sore within 6 weeks.
- Have been using hair removing creams, hair dyes, self-tanning creams, or have had electrolysis within 2 weeks prior to the peel.
- Caution is recommended for insulin-dependent diabetics.
- Anyone allergic to ASA (aspirin) should not have a salicylic acid peel
- Anyone allergic to citrus fruits should not have AHA peels.
Risks Of Deep Chemical Peels
Deeper peels carry the risk of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation in darker skin types. Other risks can be systemic toxicity with high concentrations of certain agents or their use on large surface areas (eg. salicylic acid ) as excessive absorption can result in tinnitus (ringing in the ears), dizziness, and decreased hearing. Resorcinol can rarely cause methaemaglobinuria (a blood disorder) and kidney failure, or hypothyroidism; phenol has been associated with renal toxicity and permanent hypopigmentation. There have been occasional reports of flushing, palpitations and even hives, following different agents.
It should be pointed out that deep wrinkles, scarring or pigmentation can be safely addressed with fractional resurfacing lasers and/or Intense Pulsed Light in the majority of cases, thereby avoiding the risks of potential toxicity with the above chemicals… see Lasers & Light section


